Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are a cornerstone of the modern energy world, playing an important role in supporting electrical grids, improving energy efficiency, and enhancing environmental sustainability. These systems enable energy storage in multiple ways, which contributes to reducing energy loss and increasing reliance on renewable sources. In this context, we focus on three main types of batteries used in energy storage systems: lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries, and lead-acid batteries. Each type of these batteries has unique characteristics that affect their performance and efficiency in different applications.

Lithium-ion Batteries
1-Definition and Features
Lithium-ion batteries are one of the most widely used types of batteries at the present time. They are widely used in various applications such as smartphones, laptops, and large energy storage systems. The reason for their popularity is the high energy density they provide, which means that they can store a large amount of energy in a relatively small volume. They also have a long life compared to other types of batteries, making them an attractive economic option in the long run.
Another advantage of lithium-ion batteries is that their costs have decreased significantly in recent years. This decrease in costs is the result of technological developments and improvements in manufacturing processes, making them more applicable to a wide range of applications. In addition, lithium-ion batteries provide high efficiency in converting and storing energy, which enhances their effectiveness in improving the performance of electrical grids.
Applications and uses
Lithium-ion batteries are used in energy storage systems to meet various needs, ranging from small applications such as personal electronic devices, to large systems used in electrical grids. In the context of electrical grids, these batteries can be used to store energy generated from renewable energy sources such as solar and wind energy, and then release this energy when needed to improve grid stability and provide power during peak times.
Limitations and challenges
Despite their many benefits, lithium-ion batteries face some challenges. Among them are manufacturing costs, which are still relatively high compared to some other types of batteries, despite their decrease in recent years. Additionally, these batteries can face safety issues, as they can cause fire or explosion if not handled properly or if damaged. The process of recycling lithium-ion batteries can also be complex and require special techniques, which can lead to additional environmental challenges.
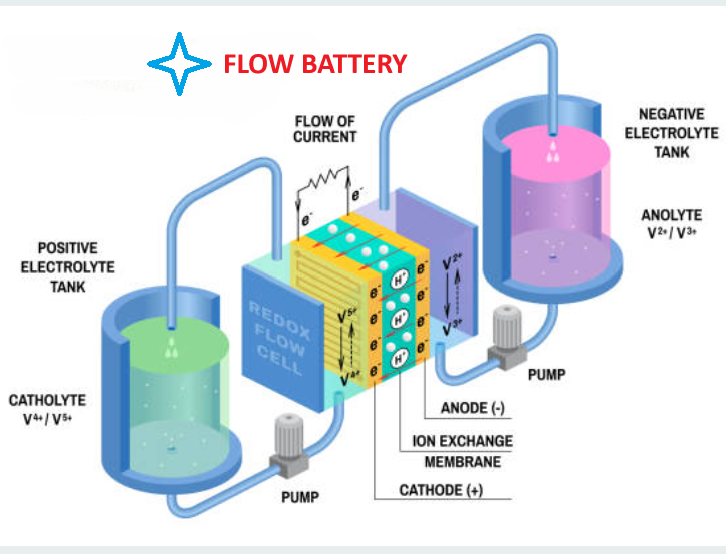
2-Flow Batteries
Definition and Features
Flow batteries are a type of battery that uses liquid electrolytes to store energy. These batteries are characterized by their ability to provide a long cycle life, which means that they can be charged and discharged repeatedly without significantly losing their storage capacity. In addition, flow batteries offer scalability that can meet large energy storage requirements, making them a suitable option for large projects and facilities that need to store large amounts of energy.
One of the notable advantages of flow batteries is their ability to handle large amounts of energy without being significantly affected by charging and discharging processes. The system size can be easily modified by increasing or decreasing the amount of electrolytes, providing great flexibility in design and operation.

Applications and Uses
Flow batteries are mainly used in large energy storage applications such as electric utilities and renewable energy plants. These batteries provide an effective solution for storing energy generated from sources such as solar and wind, and then using it in times of need to ensure grid stability and provide power during peak times. In addition, flow batteries are sometimes used to store energy in independent power projects such as large solar or wind farms.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite their many advantages, flow batteries face some challenges. Among these challenges is the high cost of the technology compared to some other types of batteries. The maintenance and management of these batteries can also be complex and require special techniques. In addition, flow batteries may face efficiency issues compared to some other types of batteries, which may affect their performance in some applications.
3-Lead Acid Batteries
Definition and Advantages
Lead acid batteries are one of the oldest types of batteries used in energy storage. These batteries are characterized by their low cost compared to other types of batteries, making them an attractive option for some budget-constrained applications. The manufacturing process is also relatively simple, which helps reduce production costs.
Applications and Uses
Lead-acid batteries are used in a wide range of applications, including backup power systems, vehicle operation, and industrial applications. These batteries are a popular choice in systems that require short-term power, such as utility backup power systems and electronic devices. Lead-acid batteries are also widely used to power vehicles such as cars and trucks.
Limitations and Challenges
Lead-acid batteries face several limitations and challenges. Among them is their low energy density compared to some other types of batteries, which means they need a larger volume to store the same amount of energy. In addition, lead-acid batteries have a relatively shorter lifespan, which may require them to be replaced more frequently. These batteries also contain toxic materials such as lead, which requires careful handling when storing
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.