Solar energy is one of the most abundant and cleanest energy sources on Earth. It can help you reduce your electricity bills, lower your carbon footprint, and increase your energy independence. However, solar energy is also intermittent and variable, meaning it’s not always available when you need it. That’s where solar cells come in handy.
Solar cells are devices that store excess solar energy, allowing you to use it when the sun isn’t shining. They can provide backup power during power outages, reducing your reliance on the grid and saving you money on your electricity bills. But how much do solar cells cost? Are they worth the investment? In this blog post, we’ll answer some of the most common questions about solar cells, such as:
What are solar cells and how do they work?
Solar cells are devices that store electricity generated by solar panels or other renewable energy sources.
Solar cells are different from regular batteries you use for gadgets or appliances. Solar cells are designed to store large amounts of electricity for long periods of time. They are usually connected to your solar panel system and the electric grid, forming a hybrid system that can optimize your energy use and savings.
Solar batteries can be used to power your home during power outages, reducing your reliance on the grid and saving money on your electricity bills.
Solar batteries have many benefits for your home and your wallet. Here are some of the ways solar batteries can help you:
- Power your home during power outages: Solar cells can provide backup power for your essential loads (such as lights, refrigerators, and phones) during grid outages and emergencies. This can enhance your energy security and resilience, especially in areas prone to natural disasters or unstable power grids.
- Reduced reliance on the grid: Solar cells can reduce your reliance on the grid and utility companies, giving you more control and flexibility over your energy supply and consumption. You can use solar cell electricity during peak hours, when grid electricity is more expensive and less reliable, and charge the solar cell during off-peak hours, when grid electricity is cheaper and more plentiful.
- Save on electricity bills: Solar batteries can help you save on electricity bills by allowing you to use more solar power and less grid power. You can also take advantage of time-of-use rates, net metering or demand response programs that reward you for using or exporting solar battery power at the best times.
What are the different types of solar cells and how do they compare?
There are different types of solar cells such as lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries, and salt water batteries.
Solar cells can be classified into different types based on their chemistry, structure, and functionality. Each solar cell type has its own advantages and disadvantages, such as cost, lifespan, capacity, efficiency, and environmental impact. Here are some of the most common and widely used solar cell types:
- Lead-acid batteries: Lead-acid batteries are the oldest and most mature type of solar cell. They are relatively cheap and easily recycled, but also suffer from low efficiency, short lifespan, and high maintenance. They are suitable for small-scale and low-demand applications, such as off-grid cabins or RVs.
- Lithium-ion batteries: Lithium-ion batteries are the most popular and widely used type of solar cells. They offer high performance, long durability, and low maintenance. They are compact, lightweight, and versatile for a variety of applications, such as residential, commercial, and industrial. However, they are also more expensive, temperature sensitive, and difficult to recycle.
- Flow Batteries: Flow batteries are a new type of solar cell. They use liquid electrolytes stored in separate tanks and pumped through the battery to generate electricity. They have high efficiency, long life, and low degradation. They are also scalable, modular, and safe, making them ideal for large-scale and high-demand applications, such as grid-scale or utility-scale. However, they are also very expensive, bulky, and complex, requiring specialized installation and maintenance.
- Saltwater Batteries: Saltwater batteries are another relatively new and emerging type of solar cell. They use a saltwater electrolyte that is non-toxic and environmentally friendly. They are low cost, long life, and safe. They are also simple, rugged, and able to withstand temperature and depth of discharge. However, they also have low efficiency, low power density, and limited availability, making them less suitable for high performance and demanding applications.
The most common and widely used type of solar cell is the lithium-ion battery, which offers high performance, long durability, and low maintenance costs.
Lithium-ion batteries are the dominant type of solar cells in the market, accounting for more than 90% of global solar cell installations in 2020. Lithium-ion batteries have several advantages over other types of solar cells, such as:
- High efficiency: Li-ion batteries have an average round-trip efficiency of 90%, which means they can deliver 90% of their stored energy. This is much higher than other types of solar cells, such as lead-acid (70%) or liquid flow (80%).
- Long life: The average life of a lithium-ion battery is 10 to 15 years, depending on use and maintenance. This is much longer than the life of other types of solar cells, such as lead-acid batteries (3 to 5 years) or flow batteries (5 to 10 years).
- Low maintenance: Lithium-ion batteries require very little maintenance as they do not require regular watering, cleaning or equalization. They also have a built-in battery management system that monitors and protects the battery from overcharging, over-discharging, overheating or short circuiting.
- Compact and lightweight: Lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, which means they can store more energy in a smaller, lighter package. This makes them easier to install and transport, and better suited for applications where space is limited, such as residential or commercial.
How much do solar cells cost? What factors affect the price?
The cost of solar cells depends on a variety of factors, such as the type, size, brand, quality, and installation of the cell.
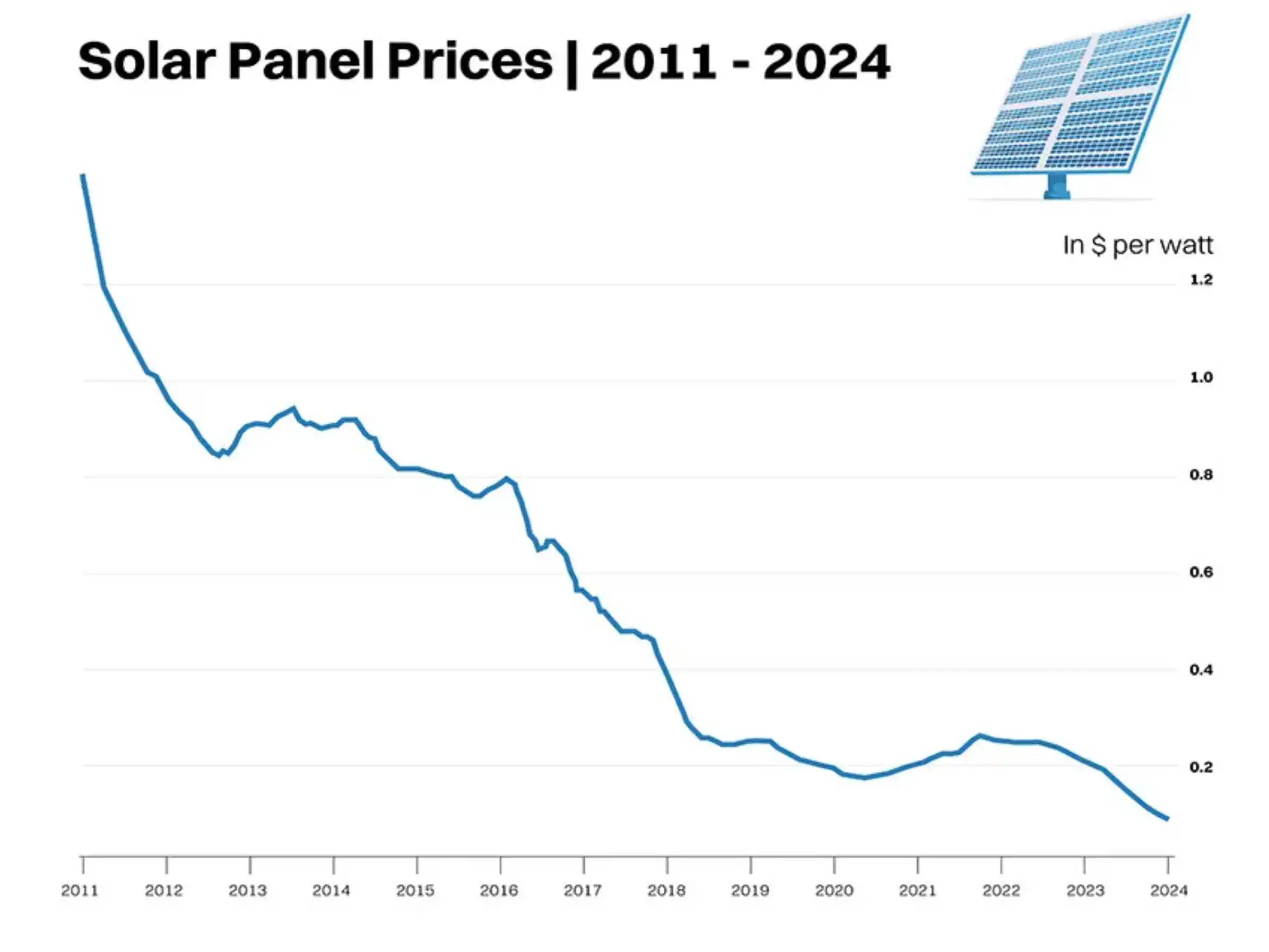
Solar cells are not cheap, and they can add significantly to the overall cost of a solar panel system. The cost of solar cells depends on a variety of factors, such as:
- Types of solar cells: As we mentioned before, there are different types of solar cells, each with a different price range. For example, lead-acid batteries are the cheapest, costing around $200 to $300 per kWh, while lithium-ion batteries are the most expensive, costing around $800 to $1,200 per kWh. Flow batteries and saltwater batteries are somewhere in between, costing around $500 to $800 per kWh.
- Solar cell size: The size of a solar cell refers to the amount of energy it can store and provide, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). The larger the size of the solar cell, the more energy it can store and the more power it can provide, but it also costs more. The size of solar cell you need depends on your energy consumption and the size of your solar panel system. For example, if you have a 5 kW solar panel system and you want to store 50% of the solar energy you generate, you will need a 10 kWh solar cell.
- Solar cell brand: The brand of a solar cell refers to the manufacturer or supplier of the solar cell. There are many brands of solar cells on the market, each with a different reputation, quality, and warranty. Some of the most popular and reputable solar cell brands include Tesla, LG, Sonnen, and Enphase. The solar cell brand you choose will affect the price, performance, and reliability of your solar cell system.
- Solar cell quality: Solar cell quality refers to the technical specifications and characteristics of solar cells, such as efficiency, lifespan, capacity, discharge rate, attenuation rate, etc. The higher the quality of the solar cell, the better the performance and longer the service life, but the higher the cost. The quality of solar cells will be affected by the type, brand and manufacturing process of the solar cell.
- Solar Installation: Solar installation refers to the process and cost of installing solar cells to your solar panel system and the electrical grid. Solar installation can be complex and challenging, requiring professional and certified installers and electricians. Solar installation may also involve additional equipment and materials, such as wiring, inverters, controllers, and meters. Solar installation may vary depending on the type, size, and location of the solar cell, as well as local regulations and incentives.
In the United States, the average cost of a solar cell is about $10,000, but can range from $5,000 to $20,000 or more depending on the factors mentioned above.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, the average cost of a 10,000 solar cell in the U.S. in 2020 was about $5,000, but it can range from $20,000 to $5,000 or even more, depending on the factors mentioned above. For example, a 10 kWh lithium-ion solar cell from Tesla costs about $14,000, while a 10 kWh lead-acid solar cell from SimpliPhi costs about $6,000. The cost of solar cells also varies by location, as different states and regions have different incentives, rebates, and taxes on solar cell systems. For example, in California, you can get a rebate of up to $3,000 for installing solar cells through the Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP), while in New York, you can get a tax credit of up to $5,000 for installing solar cells through the New York Solar Program.
Solar cell prices by brand
| brand | Brand Index | Price Range ($/Watt) |
|---|---|---|
| LONGi | 93.5 | 0.42 – 0.50 |
| JinkoSolar | 92.5 | 0.40 – 0.48 |
| TRW | 91.3 | 0.38 – 0.46 |
| J A | 90 | 0.36 – 0.44 |
| Midwest Solar Energy | 88.6 | 0.34 – 0.42 |
| resurrection | 87.4 | 0.32 – 0.40 |
| astronomy | 86.3 | 0.30 – 0.38 |
| Taiwan Solar Energy | 85.2 | 0.28 – 0.36 |
| Suntech | 84 | 0.26 – 0.34 |
| Dasola | 82.6 | 0.24 – 0.32 |
Are solar batteries worth it?
Solar cells are an investment worth considering. Not only do they harness the endless solar energy and reduce reliance on fossil fuels, but they can also significantly reduce your long-term electricity bills. If you live in an area with high electricity prices and your roof is sunny and free of shadows, then solar cells can provide you with steady energy savings. In addition, government tax incentives and subsidies may further reduce the cost of installation. Although the initial investment may be high, solar cells have a lifespan of up to 25 years and low maintenance costs, which can provide a significant financial return. At the same time, they can increase the value of a home, as more and more homebuyers are willing to pay a premium for a home that uses clean energy. Taking all these factors into consideration, if the payback period is within an acceptable range, then installing solar cells is definitely a wise choice.