Solar panels can range in price from $17,500 to $24,500. Generally speaking, the average cost of a solar system with an average power of 7kW: around $19,390. We found that the price of solar panels is affected by a variety of factors, including your region, the size of the system, and the type of panels. Given the many factors that affect the final price, having an accurate understanding of the likely costs will help you budget for solar panels to achieve the best energy savings.
| Year | Price per kW (USD) |
| 2018 | $3,200 – $3,500 |
| 2019 | $2,900 – $3,200 |
| 2020 | $2,800 – $3,100 |
| 2021 | $2,900 – $3,200 |
| 2022 | $3,000 – $3,300 |
| 2023 | $3,000 – $3,100 |
| 2024 | $3,000 – $3,100 |
Average Cost of Solar Panels
The cost of a 7kW solar system in the United States will vary by region. Based on 2023 data, the average cost is about $2.77 per watt, so the total cost of a 7kW system is about $19,390. After taking into account the federal solar tax credit, the cost may drop to $14,349.1, however, this price does not include any additional state subsidies or incentives.
Specific to each state, for example:
In Arizona, the price range is between $14,490 and $18,130.
In California, the price range is between $16,800 and $20,860.
Data from other sources suggests that the national average cost may be between $17,500 and $24,500, with most homeowners paying around $21,000.2. Still others say the average cost is around $14,000.3.
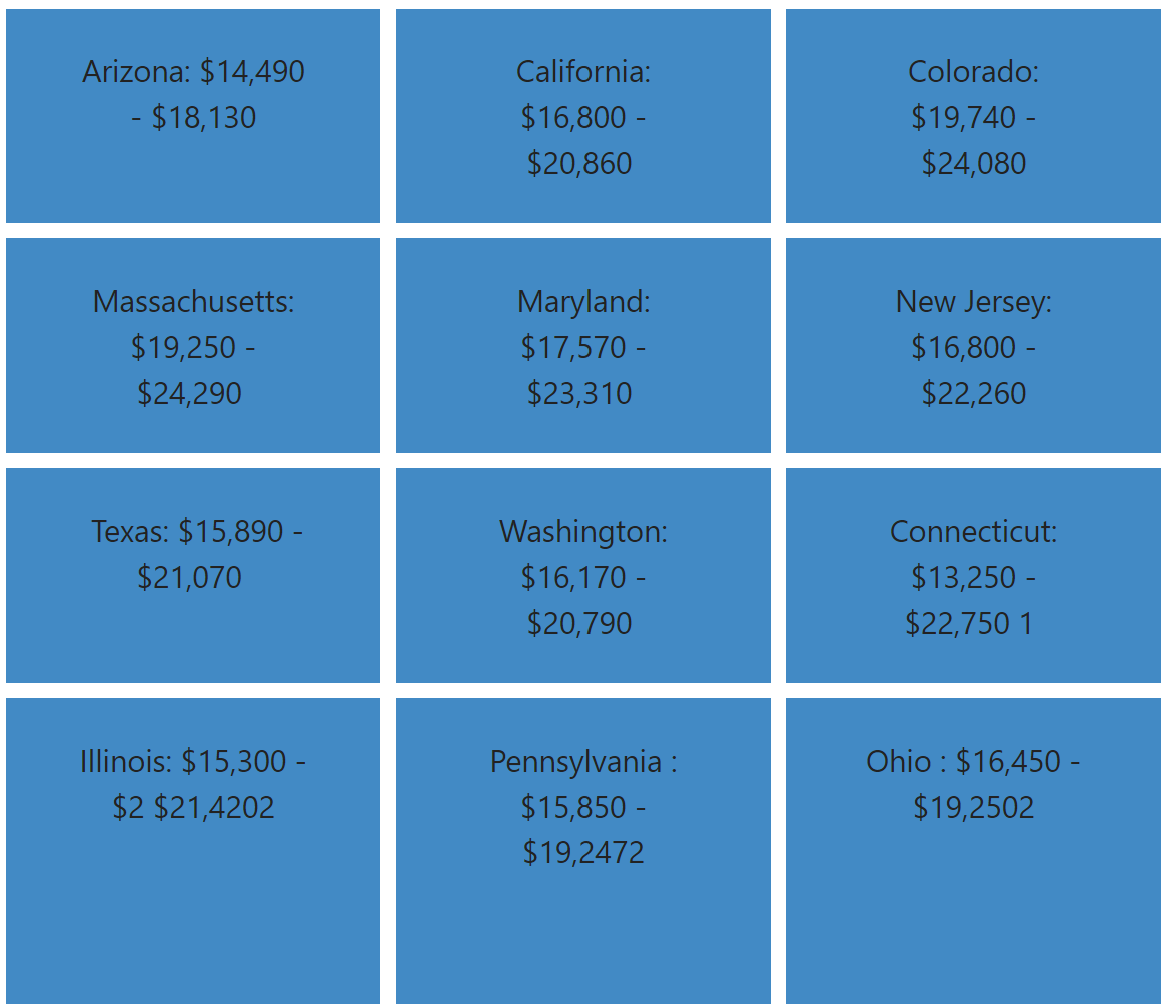
Solar panel costs in some states
Arizona: $14,490 – $18,130
California: $16,800 – $20,860
Colorado: $19,740 – $24,080
Florida : $14,980 – $19,180
Massachusetts: $19,250 – $24,290
Maryland: $17,570 – $23,310
New Jersey: $16,800 – $22,260
New York : $18,970 – $25,270
Texas: $15,890 – $21,070
Washington: $16,170 – $20,790
Connecticut: $13,250 – $22,750 1
Georgia: $14,750 – $24,850 2
Illinois: $15,300 – $2 $21,4202
Pennsylvania : $15,850 – $19,2472
Ohio : $16,450 – $19,2502
Cost Analysis of Different Types of Solar Panels
When considering solar panels as a sustainable energy solution, it’s important to understand the costs of different types of panels. Below we’ll explore the costs of three different types of solar panels and provide some considerations when buying one.
Monocrystalline Solar Panel Cost
Monocrystalline solar panels are known for their high efficiency but are correspondingly more expensive. According to market data, monocrystalline panels cost about $0.50 to $1 per watt. Despite the larger initial investment, the long-term performance of monocrystalline panels may result in greater energy savings.
Polycrystalline Solar Panel Cost
Polycrystalline solar panels offer a more cost-effective alternative. They typically cost between $0.30 and $0.80 per watt, and while slightly less efficient than monocrystalline panels, they can be a more affordable option for a home or business on a budget.
Thin Film Solar Panel Cost
Thin-film solar panels are attractive to many consumers for their low cost and flexibility. These panels cost about $0.20 to $0.50 per watt, making them the cheapest of all types. However, they are also generally the least efficient, meaning more area may be needed to generate the same amount of electricity.
When choosing solar panels, in addition to cost, other factors should be considered, such as installation location, climate conditions, available space, and expected energy needs. In addition, installation and maintenance costs are also important factors in determining the total cost.
What factors determine the cost of solar panels?
Panel Type
The type of solar panel is a major factor affecting cost. There are three main types of solar panel panels currently on the market: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels. Monocrystalline panels are known for their high efficiency and stability, but are relatively expensive to manufacture. On the other hand, polycrystalline panels strike a balance between cost and efficiency, while thin-film panels are favored in certain applications due to their low cost and flexibility.
Production scale
The scale of production is also an important factor. Large-scale production can reduce unit costs because fixed costs (such as equipment depreciation and research and development) can be spread over more products. In addition, purchasing raw materials in large quantities usually results in better prices.
Installation Method
How solar panels are mounted also affects the cost. Ground-mounted systems are generally less expensive but may require more land. Roof-mounted systems save space but are more expensive to install. Floating-mounted systems are an emerging technology on the surface of water bodies, and their costs vary with the maturity of the technology.
Geographical and climatic factors
Geographic location and climatic conditions have a significant impact on the cost and efficiency of solar panels. The intensity and availability of solar radiation determine the design of the panels and their ability to generate electricity. In addition, the tilt angle of the panels needs to be optimized according to the geographical location to maximize the energy captured.
Technology and efficiency
The efficiency of solar cells is another key factor. Efficient panels can generate more electricity in a smaller area, but this usually means higher manufacturing costs. In addition, maximum output power tracking (MPPT) technology ensures that the panels are always operating at the maximum power point, thereby improving the efficiency of the entire system.
System Components and Losses
The efficiency of other components in the system, such as the solar inverter and controller, as well as line losses and combined losses, also affect the total cost of a solar panel system. Battery efficiency is especially important for systems that require energy storage.
Maintenance and Cleaning
Maintenance and cleaning of solar panels is also part of the cost. Dust and contaminants reduce the efficiency of the panels, so regular cleaning is required to maintain optimal performance.
Market and policy
Market demand, policy support and supply chain security also affect the cost of solar panels. Government subsidies and tax incentives can reduce users’ procurement costs, while fluctuations in raw material prices and supply chain disruptions can lead to higher costs.
Can solar panels increase the value of a home?
Solar panels can add value to a home, but the exact amount depends on a variety of factors, including geographic location, energy market trends, the quality and performance of the solar panels, the value of the home itself, etc. In general, solar panels can have a positive impact on potential buyers by increasing the curb appeal and sustainability of a home, but not all potential buyers are willing to pay the extra cost for them.
There are some studies and data that show that installing solar panels can increase the value of a home to a certain extent. For example, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in the United States once conducted a study that showed that for every dollar saved on electricity bills, the value of the property will increase by $20. If a solar panel system saves you $1,000 per year, your property value will increase by $20,000. This is why homes with solar panels are usually able to sell for a higher price in the sales market. However, the specific amount of this added value varies from region to region.
How much does a solar panel roof cost?
The cost of installing a solar panel roof varies widely, depending on several factors, such as the size of the roof, the type and quality of solar panels used, installation labor costs, location, and other equipment required (such as inverters and mounting hardware).
The average cost of a residential solar panel system in the U.S. is generally $25,000 to $5,000 for a typical 15,000 kW system (not taking into account any incentives or tax credits). If the system is larger or the installation process is more complex, the cost may be higher.
It’s worth noting that there are often incentives available to help offset the cost of installing solar panels, such as federal tax credits, state and local incentives, and net metering programs. These incentives can significantly reduce upfront costs and make solar more affordable for homeowners.
2 thoughts on “Solar Panel Cost Guide 2024”