Welcome to our comprehensive guide to solar panel tax credits. As a website owner in the solar industry, it is vital to understand the nuances of tax incentives associated with solar panel installations. Solar panel tax credits play a key role in promoting the adoption of renewable energy while providing financial benefits to homeowners and businesses alike.
Federal Solar Tax Credit

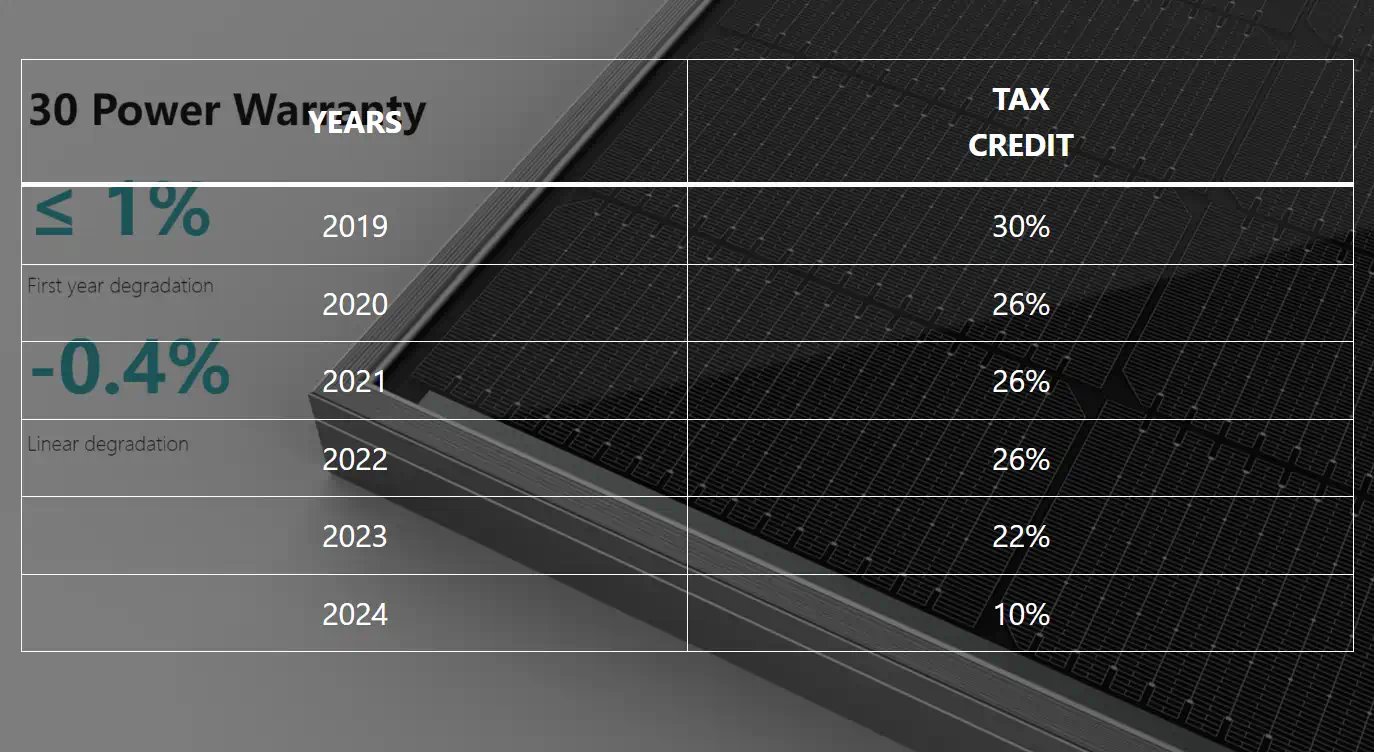
| YEARS | TAX CREDIT |
|---|---|
| 2019 | 30% |
| 2020 | 26% |
| 2021 | 26% |
| 2022 | 26% |
| 2023 | 22% |
| 2024 | 10% |
What is the Solar Panel Tax Credit?
Solar panel tax credits, also known as solar investment tax credits (ITCs), are financial incentives provided by the government to encourage the adoption of solar energy systems. These credits allow taxpayers to deduct a portion of the cost of installing solar panels from their federal or state income taxes. These incentives mainly aim to stimulate investment in renewable energy infrastructure and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
The concept of a solar panel tax credit originated as part of a broader renewable energy policy aimed at combating climate change and promoting energy independence. In the United States, the federal government introduced the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) to include solar energy in the Energy Policy Act of 2005, providing a major boost to the solar industry.
Solar panel tax credits are typically structured as a percentage of the total cost of solar panels installed, with the exact percentage varying based on factors such as location, system size, and eligibility criteria. These credits can significantly reduce the upfront cost of solar energy, making renewable energy more accessible to homeowners, businesses, and communities.
Additionally, solar panel tax credits often come with expiration dates or phase-out schedules, underscoring the importance of timely adoption and implementation of solar projects.
How does the solar panel tax credit affect you?
Solar panel tax credits have a direct impact on individuals, businesses, and the economy as a whole. Understanding how these incentives affect you can help you make informed decisions about solar investments and financial planning.
Financial impact
Solar panel tax credits reduce the overall cost of solar panel installation, providing significant financial benefits to homeowners and businesses. By offsetting some of the upfront costs, these credits make solar more affordable and economically viable in the long run. Homeowners can enjoy lower electricity bills and higher property values, while businesses can benefit from reduced operating costs and enhanced sustainability credentials.
Save tax
One of the most significant advantages of solar panel tax credits is that they have the potential to generate significant tax savings. Qualifying taxpayers can take a percentage of their solar investment as a credit against their federal or state income taxes. These credits can significantly reduce tax liabilities, allowing individuals and businesses to retain more of their earnings and reinvest them in their property or operations.
Economic stimulus
In addition to personal tax benefits, the solar panel tax credit contributes to broader economic stimulus by driving investment and job creation in the renewable energy sector. The growth of the solar industry creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and related services. In addition, increased demand for solar products and services spurs innovation and technological progress, further promoting economic growth and competitiveness.
Environmental impact
Beyond financial considerations, solar panel tax credits play a vital role in mitigating environmental degradation and combating climate change. By incentivizing the adoption of clean, renewable energy, these credits help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and reliance on finite fossil fuels. The transition to solar energy promotes sustainability and resilience in the face of environmental challenges, creating a healthier, more sustainable planet for future generations.
Social Benefits
Solar panel tax credits also provide social benefits by democratizing access to clean energy and empowering communities to take control of their energy future. By making solar more affordable and accessible, these incentives enable homeowners, businesses, and communities to reduce their carbon footprint, increase energy security, and contribute to local economic development. Additionally, solar installations can improve energy equity by providing renewable energy options to underserved populations and marginalized communities.
Who Qualifies for Solar Panel Tax Credits?
Determining eligibility for solar panel tax credits is critical for individuals and businesses considering a solar investment. Various criteria must be met to qualify for these incentives, ensuring they are allocated to projects that contribute to renewable energy adoption and sustainable development goals.
Residency Qualifications
Homeowners interested in applying for a solar panel tax credit must meet specific eligibility requirements set by a government agency or regulator. Typically, eligibility criteria include owning and occupying the property where the solar panels are installed, ensuring that the tax credit applies to a primary residence, rather than an investment property or rental unit. Additionally, the solar system must meet certain performance and quality standards to qualify for the tax credit.
Business Qualifications
Businesses, including commercial businesses, nonprofit organizations, and government entities, may also qualify for solar panel tax credits. Qualification criteria for commercial installations may differ from residential requirements and often depend on factors such as the type of business, the size of the solar system, and the nature of the project. Businesses seeking tax credits should consult with a tax professional or renewable energy expert to ensure they meet eligibility criteria and maximize their financial benefits.
Geographical factors
Solar panel tax credits are not geographically limited, and eligibility criteria vary by region, state, or jurisdiction. Some regions may offer more generous incentives or additional rebates for solar projects, while others may have stricter eligibility requirements or lower credit percentages. It is critical for individuals and businesses to research local regulations and incentives before pursuing a solar installation to ensure it meets all applicable standards and maximizes available benefits.
Time and Deadline
Timing is another key factor in determining eligibility for solar panel tax credits. These incentives often have an expiration date or phase-out schedule, meaning that the installation must be completed and operational by a specific deadline to qualify for the credit. Missing a deadline or not adhering to an application timeline can result in the loss of tax benefits, highlighting the importance of timely planning and execution of solar projects.
Documentation and Compliance
To qualify for the solar panel tax credit, individuals and businesses must maintain accurate records and documentation throughout the installation process. This includes invoices, receipts, contracts, and documentation that meets eligibility criteria and regulatory requirements. Failure to provide adequate documentation or meet compliance standards may result in disqualification or delay in receiving the tax credit.
How do I apply for a solar panel tax credit?
Applying for solar panel tax credits involves multiple steps and requires careful attention to detail to ensure eligibility and compliance. Understanding the application process is critical for individuals and businesses seeking to obtain these incentives and maximize their financial benefits.
Pre-installation planning
Before applying for a solar panel tax credit, individuals and businesses must first conduct thorough pre-installation planning to assess their energy needs, evaluate their solar energy potential, and select the appropriate equipment and installation options. This includes determining the size and capacity of the solar system, determining the best location for the solar panels, and obtaining the necessary permits and approvals from local authorities.
Select a qualified installer
Selecting a qualified, reputable solar installer is critical to ensuring project success and eligibility for tax credits. Individuals and businesses should research potential installers, request multiple quotes, and verify credentials, certifications, and customer reviews before making a decision. Working with an experienced professional can help streamline the installation process, minimize risk, and maximize the performance and lifespan of your solar system.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Throughout the installation process, individuals and businesses must maintain accurate records and documentation to support their claim for solar panel tax credits. This includes invoices, receipts, contracts, permits, inspection reports, and any other relevant documentation that demonstrates compliance with eligibility criteria and regulatory requirements. Organizing and retaining these documents is critical to substantiating expenses and proving the legitimacy of your solar project.
Filing a tax return
Once a solar energy system is installed and in operation, individuals and businesses can claim the solar panel tax credit when filing their federal or state income tax return. The process for claiming the tax credit may vary by jurisdiction and tax filing status, so it is important to consult a tax professional or use tax preparation software to ensure that your tax return is filed accurately and on time. Taxpayers should carefully review the tax forms, instructions, and guidance related to renewable energy incentives to properly claim the credit.
Monitoring and Compliance
After applying for a solar panel tax credit, individuals and businesses should monitor their compliance with ongoing requirements and obligations to remain eligible for the tax benefit. This may include regular inspections, reporting obligations, or compliance with performance standards set by regulators or incentive programs. Staying abreast of regulatory changes and updates is critical to ensuring ongoing compliance and maximizing the long-term benefits of your solar investment.
How much is the solar panel tax credit?
Understanding the amount of the solar panel tax credit available is critical for individuals and businesses to assess the financial viability of a solar project. The credit amount directly affects the overall cost-effectiveness and return on investment of a solar installation, influencing decision making and project planning.
Percentage-based credits
Solar panel tax credits are typically calculated as a percentage of the total cost of solar panel installation. The exact percentage depends on factors such as jurisdiction, tax laws, and eligibility criteria. For example, in the United States, the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) provides a credit equal to a certain percentage of qualified expenditures for solar energy systems installed on residential and commercial properties. Through 2024, the federal ITC provides a credit of 26% for solar projects placed in service before March 31, 2022. However, it is worth noting that the credit percentage may vary in subsequent years because the ITC is subject to predetermined phases under current legislation.
Maximum credit limit
In addition to percentage-based credits, solar panel tax credits may impose maximum credit limits on qualifying expenditures. These limits restrict the total amount of tax credits that can be claimed for a particular solar project, regardless of the actual installation cost. For example, the federal ITC imposes maximum credit limits on residential solar projects based on installed capacity, while commercial projects have no maximum credit limit. It is critical for taxpayers to understand these limits when planning and budgeting for solar installations to ensure they can maximize available credits within the specified thresholds.
Calculate credit amount
Calculating the amount of the solar panel tax credit requires careful consideration of eligible expenses, the credit percentage, and any applicable maximum credit limits. Taxpayers can generally claim credits for eligible expenses related to solar panel equipment, installation labor, permit fees, and other direct costs associated with a solar energy system. By multiplying eligible expenses by the applicable credit percentage, taxpayers can determine the total amount of credit available for their solar project. It is critical to maintain accurate records and documentation during tax time to support these calculations and substantiate credit claims.
The impact of gradual reduction
It is important to note that the solar panel tax credit may be phased down or reduced over time as part of legislative or regulatory changes. For example, the federal ITC is scheduled to phase down gradually, with the credit percentage decreasing from 26% to 22% for projects placed in service in 2023 and 2024, respectively. Taxpayers should consider the impact of these phase-downs when planning their solar installation and tax credit budgets, as the reduction in the tax credit percentage may affect the overall financial return on a solar investment.
State and local incentives
In addition to federal tax credits, individuals and businesses may be eligible for state and local incentives to further reduce the cost of installing solar panels and increase overall financial benefits. State-specific tax credits, rebates, grants, and performance-based incentives can supplement federal incentives, provide additional savings, and increase the affordability of solar projects. Taxpayers should research the incentives available in their respective jurisdictions and explore opportunities to stack multiple incentives to achieve the greatest financial impact.
What is the time limit on the solar panel tax credit?
Understanding the time limits associated with solar panel tax credits is critical for individuals and businesses planning solar projects. Time limits can impact eligibility, application deadlines, and overall financial viability of solar installations, so careful consideration and timely action are required.
Date of Expiry
Solar panel tax credits often have expiration dates or sunset clauses that specify when the installation must be completed to qualify for the credit. These expiration dates are often established by legislation or regulatory agencies and can vary by jurisdiction and incentive program. For example, the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) for solar installations in the United States sets specific deadlines for claiming the credit once the project is placed in service. Missing these expiration dates can result in the loss of tax benefits, highlighting the importance of timely planning and execution of solar projects.
Elimination schedule
In addition to the expiration date, the solar panel tax credit may be subject to a phase-out, or reduction over time. Phase-out schedules gradually reduce the percentage of the credit available for qualified expenditures, so taxpayers must consider the impact of these reductions when planning solar installations. For example, under current legislation, the federal ITC phases in lower percentages of the credit for projects placed in service after certain deadlines. Taxpayers should be aware of these phase-out schedules and adjust their project schedules accordingly to maximize the available credit.
Retroactive extension
In some cases, the solar panel tax credit may be retroactively extended or amended through legislative action or policy changes. Retroactive extensions allow taxpayers to claim the credit for installations completed within a specified time frame, even if the original expiration date has passed. These extensions provide taxpayers with flexibility and the opportunity to benefit from tax incentives retroactively, but also require careful monitoring of legislative developments and timely action to take advantage of available tax credits. Taxpayers should stay informed of potential retroactive extensions and consult a tax professional to assess their eligibility and filing options.
Continuous monitoring
Given the dynamic nature of renewable energy policy and tax incentives, ongoing monitoring of regulatory developments and program updates is critical for individuals and businesses seeking to maximize their solar panel tax credits. Changes in legislation, administrative guidance, or market conditions may impact eligibility criteria, credit amounts, and application procedures, requiring ongoing evaluation and adjustments to solar projects. Taxpayers should stay abreast of relevant developments from government agencies, industry associations, and advocacy groups to ensure compliance and optimize their financial benefits.
Planning and Compliance
To effectively navigate the time limits on the solar panel tax credit, individuals and businesses should prioritize proactive planning, compliance, and timely execution of solar projects. This includes conducting a thorough pre-installation assessment, selecting qualified installers, maintaining accurate documentation, and adhering to project timelines and deadlines. By planning ahead and remaining vigilant, taxpayers can reduce risk, maximize available credits, and take advantage of the transition to clean, renewable energy.
The relationship between solar panel tax credits and environmental protection
The relationship between solar panel tax credits and environmental protection is an important aspect of renewable energy policy and sustainable development efforts. Understanding how tax incentives affect environmental outcomes can provide insights into the effectiveness of policy interventions and the broader transition to clean energy.
Promoting the adoption of renewable energy
Solar panel tax credits play a key role in promoting the adoption of renewable energy technologies such as solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, making them more economically viable and attractive to homeowners, businesses and utilities. By reducing the upfront costs of solar installations, tax incentives encourage greater investment in clean energy infrastructure and accelerate the transition away from fossil fuels. This shift to renewable energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality and mitigate the impacts of climate change, thereby advancing environmental protection goals.
Mitigating climate change
One of the main environmental benefits of the solar panel tax credit is that it helps mitigate climate change by reducing reliance on carbon-intensive energy sources. Solar energy is a clean, abundant, renewable resource that produces electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other pollutants associated with the combustion of fossil fuels. By incentivizing the deployment of solar photovoltaic systems, the tax credit helps reduce overall carbon emissions from the power sector, critical to achieving emissions reduction targets set forth in international agreements such as the Paris Agreement.
Protecting Natural Resources
Solar power has minimal environmental impact compared to traditional energy sources such as coal, oil, and natural gas, which require extensive extraction, processing and combustion of finite resources. The solar panel tax credit supports the conservation of natural resources by promoting the deployment of low-impact energy technologies that use sunlight to generate electricity. In addition, solar installations typically have lower water consumption requirements and do not produce hazardous waste or air pollutants, further reducing their environmental footprint and protecting ecosystems and biodiversity.
Promoting energy independence
Solar panel tax credits contribute to energy independence and security by diversifying energy supplies and reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. By harnessing locally available sunlight to generate electricity, solar PV systems help stabilize energy prices, mitigate geopolitical risks associated with fossil fuel dependence, and increase resilience to supply disruptions. This shift toward decentralized, distributed energy generation enables communities, businesses, and governments to take control of their energy future and reduce vulnerability to external shocks such as fuel price volatility or geopolitical conflict.
Empowering sustainable development
In addition to environmental benefits, solar panel tax credits support the Sustainable Development Goals by promoting economic growth, job creation, and social equity. The expansion of the solar industry creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and related industries, stimulating economic activity and prosperity. In addition, solar projects can provide affordable electricity to underserved communities, improve energy equity, and enhance social resilience by reducing energy costs and increasing energy security for vulnerable groups.
Frequently Asked Questions About Solar Panel Tax Credits
Do I qualify for a solar panel tax credit?
Eligibility for the solar panel tax credit depends on a variety of factors, including your tax filing status, property ownership, and compliance with program requirements. Generally, homeowners, businesses, and nonprofits that install qualifying solar systems may qualify for the tax credit. It is necessary to consult a tax professional or renewable energy expert to determine your eligibility and maximize the available incentives.
What expenses qualify for the solar panel tax credit?
Expenses that qualify for the solar panel tax credit typically include solar panels., solar inverters , mounting hardware, installation labor, permit fees, and other direct costs associated with a solar energy system. In addition, certain indirect costs, such as engineering and design fees, may also qualify for credits. Keeping accurate records of all expenses is essential to substantiating credit claims and complying with program requirements.
How do I apply for a solar panel tax credit?
To claim the solar panel tax credit, you must file the appropriate tax forms with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or relevant taxing authority. Typically, you will need to complete Form 5695 ( Residential Energy Credit ) or Form 3468 ( Investment Credit ) and include the calculated credit on your federal or state income tax return. Be sure to follow the instructions provided with the tax form and keep supporting documentation in case of an audit.
What is the maximum credit amount for solar panel installation?
The maximum credit amount for solar panel installations varies based on factors such as system size, tax filing status, and applicable credit percentage. For residential installations in the U.S., the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) currently provides a credit equal to 26% of eligible expenditures for solar projects placed in service before a certain deadline. However, there may be a maximum credit limit, so it is necessary to consult a tax professional and review the program guide for an accurate calculation.
Are solar panel tax credits refundable?
In some cases, solar panel tax credits may be refundable, meaning taxpayers can get a refund for any excess credit amounts not used to offset their tax liability. However, refund provisions vary by jurisdiction and may be limited or restricted. Taxpayers should review program guidance and consult a tax professional to understand whether their credits are refundable and how to handle any excess credits.
Can I stack the solar panel tax credit with other incentives?
Yes, in many cases, solar panel tax credits can be stacked with other incentives, such as rebates, grants and performance-based incentives offered by state, local or utility programs. Stacking multiple incentives can significantly reduce the overall cost of a solar installation and improve the financial benefits to ratepayers. Be sure to explore all available incentives and opportunities to maximize the savings on your solar project.
What happens if I miss the deadline for the solar panel tax credit?
Missing the deadline for solar panel tax credits could result in losing the tax benefits for your solar project. Timely planning and execution of your installation is critical to ensure eligibility for the credits and avoid potential penalties or delays. If you are unable to meet the deadline, you may still qualify for other incentives or financing options, so be sure to explore alternative strategies to achieve your renewable energy goals.
How does the solar panel tax credit affect my tax refund?
Solar panel tax credits can have a significant impact on your tax refund by reducing your overall tax liability or providing a refund for any excess credit amounts. By claiming a credit for qualifying solar expenditures, you have the potential to lower your tax bill and increase your tax refund, providing additional funds that can be reinvested in your property or used for other purposes. Be sure to consult a tax professional to understand how the solar panel tax credit will affect your specific tax situation and financial outcomes.